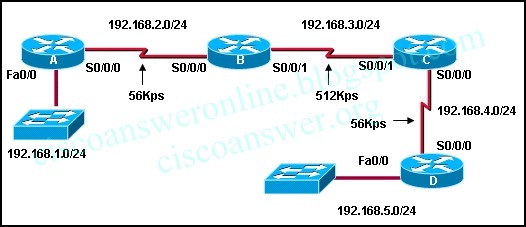
1.Refer to the exhibit.
RIPv1 is running on all three routers. All interfaces have been correctly configured with addresses in the address ranges that are shown. Which route would you see in the routing table on router CHI if the routers are configured with the commands that are displayed in the exhibit?
192.168.0.4/30
192.168.0.0/24
192.168.0.0/16
192.168.0.32/27
2.Which two statements are true regarding the characteristics of RIPv1? (Choose two).
It is a distance vector routing protocol.
It advertises the address and subnet mask for routes in routing updates.
The data portion of a RIP message is encapsulated into a TCP segment.
The data portion of a RIP message is encapsulated into a UDP segment.
It broadcasts updates every 15 seconds.
It allows a maximum of 15 routers in the routing domain.
3.What are three characteristics of the RIPv1 routing protocol? (Choose three.)
supports the use of VLSM
uses hop count as a metric
considers a metric of 16 as infinity
has an administrative distance of 110 by default
includes the destination IP address and subnet mask in routing updates
calculates metrics using the Bellman Ford algorithm
4.Refer to the exhibit.
A network consists of multiple routers. What can be verified when the show ip protocols command is issued on one of the routers in the network?
whether all routes in the network have been properly added to the routing table
routing protocol configuration in use for IP on this router
operational status of routing protocols in use on all routers in the network
routing metric of each network that is listed in the routing table
5.Refer to the exhibit.
All routers that are shown are running the RIP routing protocol. All unknown IP traffic must be forwarded to the ISP. What router or set of routers are recommended to have both a default route and the default-information originate command issued to implement this forwarding policy?
only Router1
only the gateway router
all routers in the network
only the routers with LANs needing Internet access
6.Which of the following is considered a limitation of RIP v1?
RIP v1 does not send subnet mask information in its updates.
RIP v1 is not widely supported by networking hardware vendors.
RIP v1 consumes excessive bandwidth by multicasting routing updates using a Class D address.
RIP v1 requires enhanced router processors and extra RAM to function effectively.
RIP v1 does not support load balancing across equal-cost paths.
RIP v1 authentication is complicated and time-consuming to configure.
7.Refer to the exhibit.
What can be concluded from the routing table output of router B?
A static default route has been configured on B.
The default-information originate command has been entered on A.
All traffic that is destined for 192.168.1.1 will be sent to address 0.0.0.0.
Hosts on the 10.16.1.0/27 network have 192.168.1.1 configured as the default gateway address.
8.Refer to the exhibit.
All routers are configured with valid interface addresses in the indicated networks and are running RIPv1. The network is converged. Which routes are present in the routing tables?
All routers have all routes in their routing table.
All routers have all /30 routes, but do not have /24 routes in their routing table.
All routers have all /30 routes. Routers A and E also have some of the /24 routes in their routing table.
All routers have all /30 routes. Routers B and D also have some of the /24 routes in their routing table.
Routers A and E have all routes. Routers B and D have only /30 routes in their routing table.
Routers A and E have only /24 routes. Routers B and D have only /30 routes in their routing table.
9.Which command or set of commands will stop the RIP routing process?
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# shutdown
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network no 192.168.2.0
RouterB(config)# no router rip
RouterB(config)# router no rip
10.Refer to the exhibit.
The network that is shown is running RIPv1. The 192.168.10.0/24 network was recently added and will only contain end users. What command or set of commands should be entered on Router1 to prevent RIPv1 updates from being sent to the end user devices on the new network while still allowing this new network to be advertised to other routers?
Router1(config-router)# no router rip
Router1(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
Router1(config-router)# no network 192.168.10.0
Router1(config-router)# passive-interface fastethernet 0/0
Router1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0/0/0
11.Refer to the exhibit.
Router1 and Router2 are running the RIPv1 protocol. The network administrator configures the commandnetwork 10.1.0.0 on Router1. What network will Router1 advertise to Router2?
10.1.0.0/16
10.1.0.0/8
10.0.0.0/16
10.0.0.0/8
12.Refer to the exhibit.
Router1 is running RIPv1. What command was entered into Router1 to configure the gateway of last resort?
no auto-summary
ip default-network 0.0.0.0
ip default-gateway 10.0.0.0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/1
13.What will happen if an interface IP address is entered for the address portion of the network command in a RIPv1 configuration instead of a network address?
The router will reject the command.
A route to the host address will be added to outgoing RIP updates.
A route to the host address will be added to the routing table.
All interfaces in the same classful network as the configured address will be included in the RIPv1 routing process.
14.The following line was displayed in the output of the show ip route command.
R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/3] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:30, Serial0/0
What is the value of the routing metric?
3
12
20
30
120
15.Which of the following would be the correct command sequence to enable RIP on Router B for all connected networks?
RouterB# router rip
RouterB(router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(router)# network 220.17.29.0
RouterB(router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 198.16.4.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 199.84.32.0
RouterB(config)# configure router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 199.84.32.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 198.16.4.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 198.16.4.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 220.17.29.0
16.Which command will display RIP activity as it occurs on a router?
debug ip rip
show ip route
show ip interface
show ip protocols
debug ip rip config
show ip rip database
17.Refer to the exhibit.
The Ethernet interface on Router2 goes down and the administrator notices that the route is still valid in the routing table of Router1. How much longer will it take for Router1 to mark the route invalid by setting the metric to 16?
30 seconds
90 seconds
155 seconds
180 seconds
255 seconds
18.Refer to the exhibit.
All routers in the exhibit are running RIP v1. The network administrator issues the show ip route command on router A. What routes would appear in the routing table output if the network is converged? (Choose two).
R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1]
C 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1]
R 10.10.3.0/24 [120/0]
C 10.10.3.0/24 [120/1]
R 10.10.1.0/24 [120/2]
R 10.10.1.0/24 [120/3]
19.What is the default update period in seconds for the RIP routing protocol?
10
12
15
20
30
60
RIPv1 is running on all three routers. All interfaces have been correctly configured with addresses in the address ranges that are shown. Which route would you see in the routing table on router CHI if the routers are configured with the commands that are displayed in the exhibit?
192.168.0.4/30
192.168.0.0/24
192.168.0.0/16
192.168.0.32/27
2.Which two statements are true regarding the characteristics of RIPv1? (Choose two).
It is a distance vector routing protocol.
It advertises the address and subnet mask for routes in routing updates.
The data portion of a RIP message is encapsulated into a TCP segment.
The data portion of a RIP message is encapsulated into a UDP segment.
It broadcasts updates every 15 seconds.
It allows a maximum of 15 routers in the routing domain.
3.What are three characteristics of the RIPv1 routing protocol? (Choose three.)
supports the use of VLSM
uses hop count as a metric
considers a metric of 16 as infinity
has an administrative distance of 110 by default
includes the destination IP address and subnet mask in routing updates
calculates metrics using the Bellman Ford algorithm
4.Refer to the exhibit.
A network consists of multiple routers. What can be verified when the show ip protocols command is issued on one of the routers in the network?
whether all routes in the network have been properly added to the routing table
routing protocol configuration in use for IP on this router
operational status of routing protocols in use on all routers in the network
routing metric of each network that is listed in the routing table
5.Refer to the exhibit.
All routers that are shown are running the RIP routing protocol. All unknown IP traffic must be forwarded to the ISP. What router or set of routers are recommended to have both a default route and the default-information originate command issued to implement this forwarding policy?
only Router1
only the gateway router
all routers in the network
only the routers with LANs needing Internet access
6.Which of the following is considered a limitation of RIP v1?
RIP v1 does not send subnet mask information in its updates.
RIP v1 is not widely supported by networking hardware vendors.
RIP v1 consumes excessive bandwidth by multicasting routing updates using a Class D address.
RIP v1 requires enhanced router processors and extra RAM to function effectively.
RIP v1 does not support load balancing across equal-cost paths.
RIP v1 authentication is complicated and time-consuming to configure.
7.Refer to the exhibit.
What can be concluded from the routing table output of router B?
A static default route has been configured on B.
The default-information originate command has been entered on A.
All traffic that is destined for 192.168.1.1 will be sent to address 0.0.0.0.
Hosts on the 10.16.1.0/27 network have 192.168.1.1 configured as the default gateway address.
8.Refer to the exhibit.
All routers are configured with valid interface addresses in the indicated networks and are running RIPv1. The network is converged. Which routes are present in the routing tables?
All routers have all routes in their routing table.
All routers have all /30 routes, but do not have /24 routes in their routing table.
All routers have all /30 routes. Routers A and E also have some of the /24 routes in their routing table.
All routers have all /30 routes. Routers B and D also have some of the /24 routes in their routing table.
Routers A and E have all routes. Routers B and D have only /30 routes in their routing table.
Routers A and E have only /24 routes. Routers B and D have only /30 routes in their routing table.
9.Which command or set of commands will stop the RIP routing process?
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# shutdown
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network no 192.168.2.0
RouterB(config)# no router rip
RouterB(config)# router no rip
10.Refer to the exhibit.
The network that is shown is running RIPv1. The 192.168.10.0/24 network was recently added and will only contain end users. What command or set of commands should be entered on Router1 to prevent RIPv1 updates from being sent to the end user devices on the new network while still allowing this new network to be advertised to other routers?
Router1(config-router)# no router rip
Router1(config-router)# network 192.168.10.0
Router1(config-router)# no network 192.168.10.0
Router1(config-router)# passive-interface fastethernet 0/0
Router1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0/0/0
11.Refer to the exhibit.
Router1 and Router2 are running the RIPv1 protocol. The network administrator configures the commandnetwork 10.1.0.0 on Router1. What network will Router1 advertise to Router2?
10.1.0.0/16
10.1.0.0/8
10.0.0.0/16
10.0.0.0/8
12.Refer to the exhibit.
Router1 is running RIPv1. What command was entered into Router1 to configure the gateway of last resort?
no auto-summary
ip default-network 0.0.0.0
ip default-gateway 10.0.0.0
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 S0/0/1
13.What will happen if an interface IP address is entered for the address portion of the network command in a RIPv1 configuration instead of a network address?
The router will reject the command.
A route to the host address will be added to outgoing RIP updates.
A route to the host address will be added to the routing table.
All interfaces in the same classful network as the configured address will be included in the RIPv1 routing process.
14.The following line was displayed in the output of the show ip route command.
R 192.168.3.0/24 [120/3] via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:30, Serial0/0
What is the value of the routing metric?
3
12
20
30
120
15.Which of the following would be the correct command sequence to enable RIP on Router B for all connected networks?
RouterB# router rip
RouterB(router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(router)# network 220.17.29.0
RouterB(router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 198.16.4.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 199.84.32.0
RouterB(config)# configure router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 199.84.32.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 198.16.4.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 211.168.74.0
RouterB(config)# router rip
RouterB(config-router)# network 198.16.4.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 210.36.7.0
RouterB(config-router)# network 220.17.29.0
16.Which command will display RIP activity as it occurs on a router?
debug ip rip
show ip route
show ip interface
show ip protocols
debug ip rip config
show ip rip database
17.Refer to the exhibit.
The Ethernet interface on Router2 goes down and the administrator notices that the route is still valid in the routing table of Router1. How much longer will it take for Router1 to mark the route invalid by setting the metric to 16?
30 seconds
90 seconds
155 seconds
180 seconds
255 seconds
18.Refer to the exhibit.
All routers in the exhibit are running RIP v1. The network administrator issues the show ip route command on router A. What routes would appear in the routing table output if the network is converged? (Choose two).
R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1]
C 192.168.2.0/24 [120/1]
R 10.10.3.0/24 [120/0]
C 10.10.3.0/24 [120/1]
R 10.10.1.0/24 [120/2]
R 10.10.1.0/24 [120/3]
19.What is the default update period in seconds for the RIP routing protocol?
10
12
15
20
30
60